Creating A Sample Application
NERC's OpenShift service is a platform that provides a cloud-native environment for developing and deploying applications.
Here, we walk through the process of creating a simple web application, deploying it. This example uses the Node.js programming language, but the process with other programming languages will be similar. Instructions provided show the tasks using both the web console and the command-line tool.
Using the Developer perspective on NERC's OpenShift Web Console
-
Go to the NERC's OpenShift Web Console.
-
Click on the Perspective Switcher drop-down menu and select Developer.
-
In the Navigation Menu, click +Add.
-
Creating applications using samples: Use existing code samples to get started with creating applications on the OpenShift Container Platform. Find the Create applications using samples section and then click on "View all samples" and then select the type of application you want to create (e.g. Node.js, Python, Ruby, etc.), it will load application from Git Repo URL and then review or modify the application Name for your application. Alternatively, If you want to create an application from your own source code located in a git repository, select Import from Git. In the Git Repo URL text box, enter your git repo url. For example:
https://github.com/myuser/mypublicrepo.git. You may see a warning stating "URL is valid but cannot be reached". You can ignore this warning! -
Click "Create" to create your application.
-
Once your application has been created, you can view the details by clicking on the application name in the Project Overview page.
-
On the Topology View menu, click on your application, or the application circle if you are in graphical topology view. In the details panel that displays, scroll to the Routes section on the "Resources" tab and click on the link to go to the sample application. This will open your application in a new browser window. The link will look similar to
https://<your-application-name>-<your-namespace>.apps.shift.nerc.mghpcc.org.
Example: Deploying a Python application
For a quick example on how to use the "Import from Git" option to deploy a sample Python application, please refer to this guide.
Additional resources
For more options and customization please read this.
Using the CLI (oc command) on your local terminal
Alternatively, you can create an application on the NERC's OpenShift cluster by using the oc new-app command from the command line terminal.
i. Make sure you have the oc CLI tool installed and configured on your local
machine following these steps.
Information
Some users may have access to multiple projects. Run the following command to
switch to a specific project space: oc project <your-project-namespace>.
ii. To create an application, you will need to specify the language and runtime
for your application. You can do this by using the oc new-app command and specifying
a language and runtime. For example, to create a Node.js application, you can run
the following command:
oc new-app nodejs
iii. If you want to create an application from an existing Git repository, you can
use the --code flag to specify the URL of the repository. For example:
oc new-app --code https://github.com/myuser/mypublicrepo. If you want to use a
different name, you can add the --name=<newname> argument to the oc new-app command.
For example: oc new-app --name=mytestapp https://github.com/myuser/mypublicrepo.
The platform will try to automatically detect the programming language
of the application code and select the latest version of the base language image
available. If oc new-app can't find any suitable Source-To-Image (S2I) builder
images based on your source code in your Git repository or unable to detect the programming
language or detects the wrong one, you can always specify the image you want to use
as part of the new-app argument, with oc new-app <image url>~<git url>. If it is
using a test application based on Node.js, we could use the same command as before
but add nodejs~ before the URL of the Git repository.
For example: oc new-app nodejs~https://github.com/myuser/mypublicrepo.
Important Note
If you are using a private remote Git repository, you can use the
--source-secret flag to specify an existing source clone secret that
will get injected into your BuildConfig to access the repository.
For example: oc new-app https://github.com/myuser/yourprivaterepo --source-secret=yoursecret.
iv. Once your application has been created, You can run oc status to see if your
application was successfully built and deployed. Builds and deployments can sometimes
take several minutes to complete, so you may run this several times. you can view
the details by running the oc get pods command. This will show you a list of all
the pods running in your project, including the pod for your new application. The
oc rsh pod/<pod_name> command opens a remote shell session inside the specified
OpenShift pod i.e.
v. When using the oc command-line tool to create an application, a route is not
automatically set up to make your application web accessible. Run the following
to make the test application web accessible:
oc create route edge --service=mytestapp --insecure-policy=Redirect.
Once the application is deployed and the route is set up, it can be accessed at
a web URL similar to https://mytestapp-<your-namespace>.apps.shift.nerc.mghpcc.org.
For more additional resources
For more options and customization please read this.
Using the Developer Catalog on NERC's OpenShift Web Console
The Developer Catalog offers a streamlined process for deploying applications and services supported by Operator-backed services like CI/CD, Databases, Builder Images, and Helm Charts. It comprises a diverse array of application components, services, event sources, and source-to-image builders ready for integration into your project.
About Quick Start Templates
By default, the templates build using a public source repository on GitHub that contains the necessary application code. For more options and customization please read this.
Steps
-
Go to the NERC's OpenShift Web Console.
-
Click on the Perspective Switcher drop-down menu and select Developer.
-
In the Navigation Menu, click +Add.
-
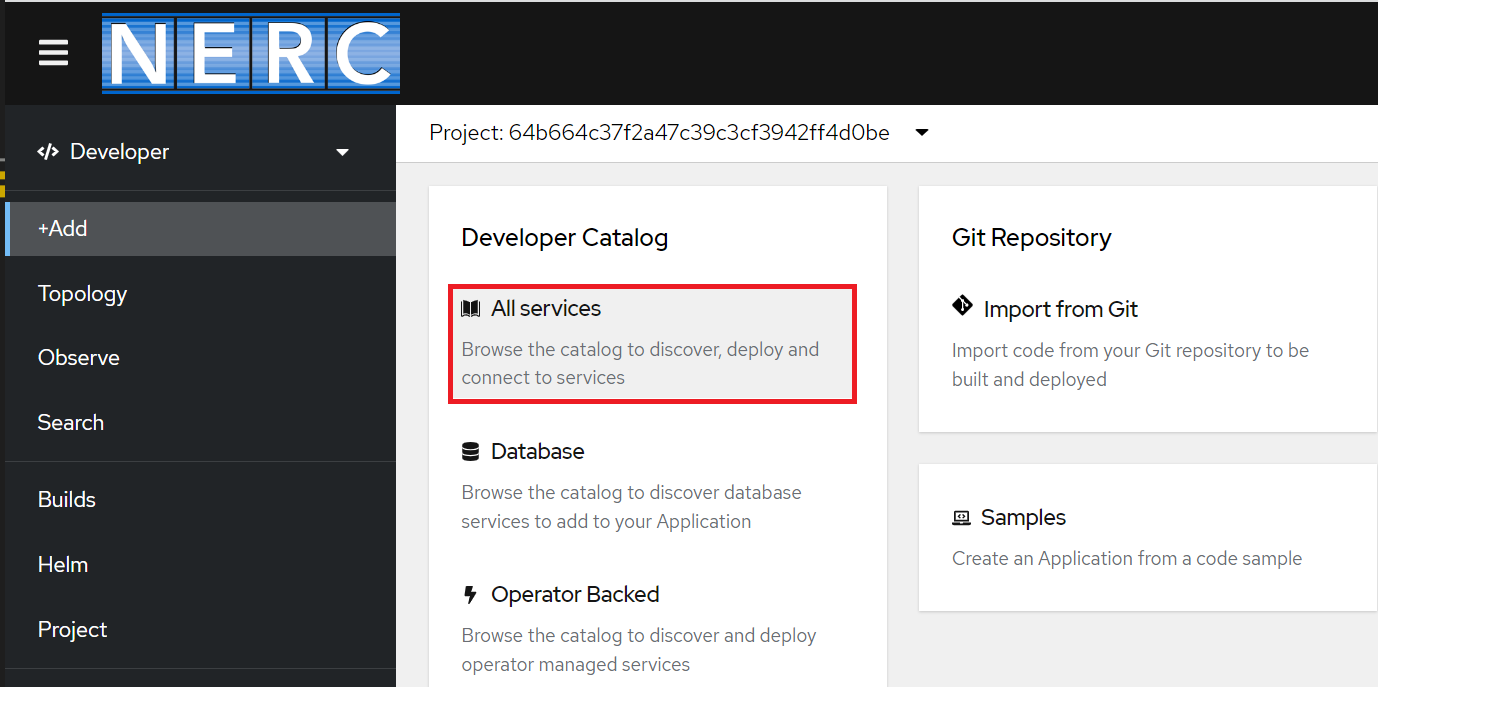
You need to find the Developer Catalog section and then select All services option as shown below:
-
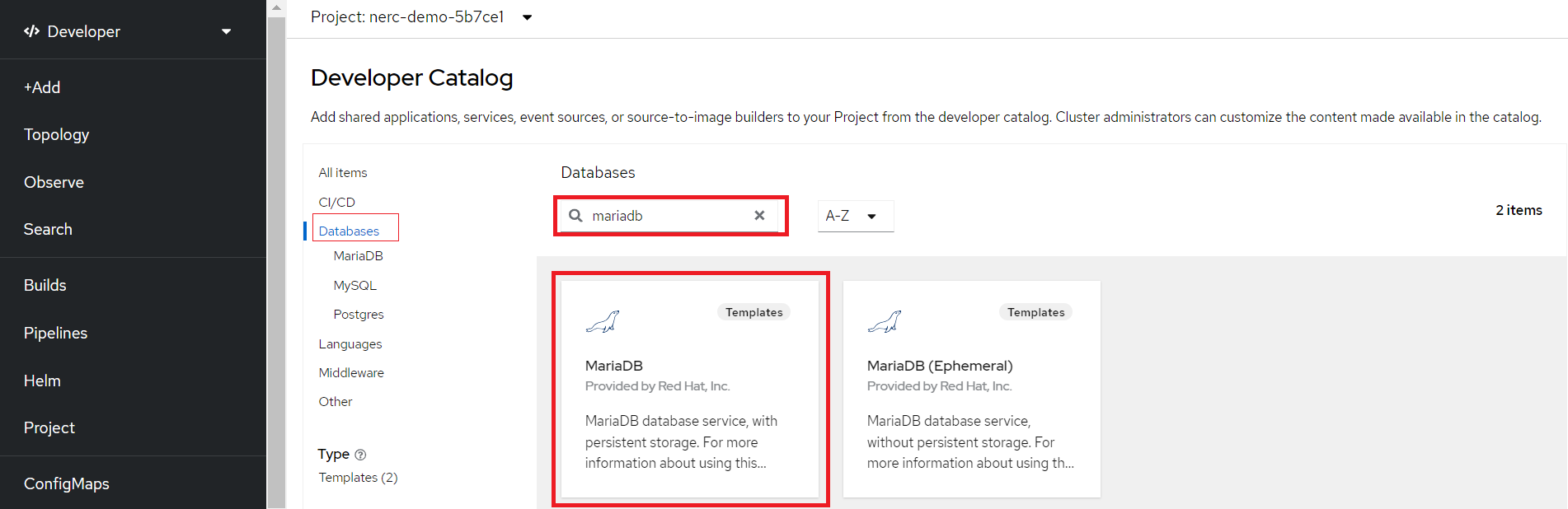
Then, you will be able search any available services from the Developer Catalog templates by searching for it on catalog and choose the desired type of service or component that you wish to include in your project. For this example, select Databases to list all the database services and then click MariaDB to see the details for the service.
To Create Your Own Developer Catalog Service
You also have the option to create and integrate custom services into the Developer Catalog using a template, as described here.
-
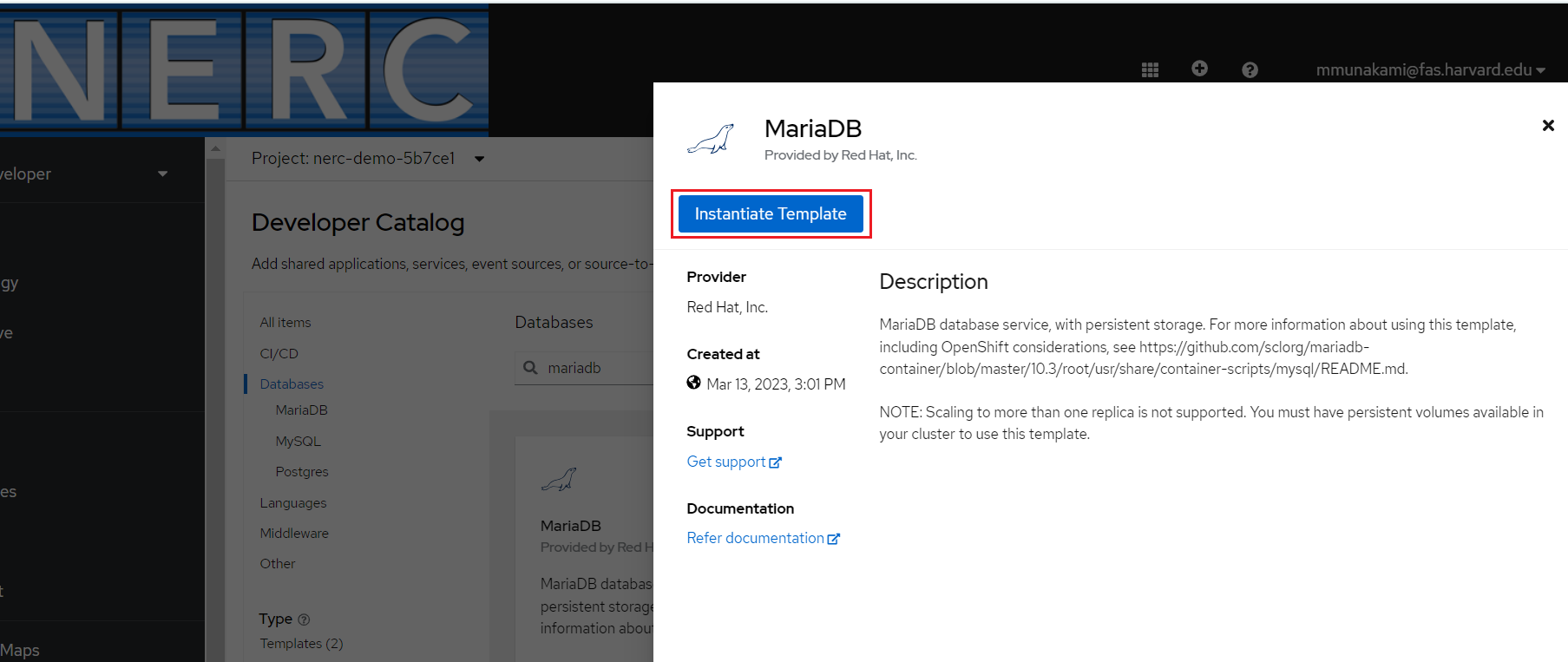
Once selected by clicking the template, you will see Instantiate Template web interface as shown below:
-
Clicking "Instantiate Template" will display an automatically populated template containing details for the MariaDB service. Click "Create" to begin the creation process and enter any custom information required.
-
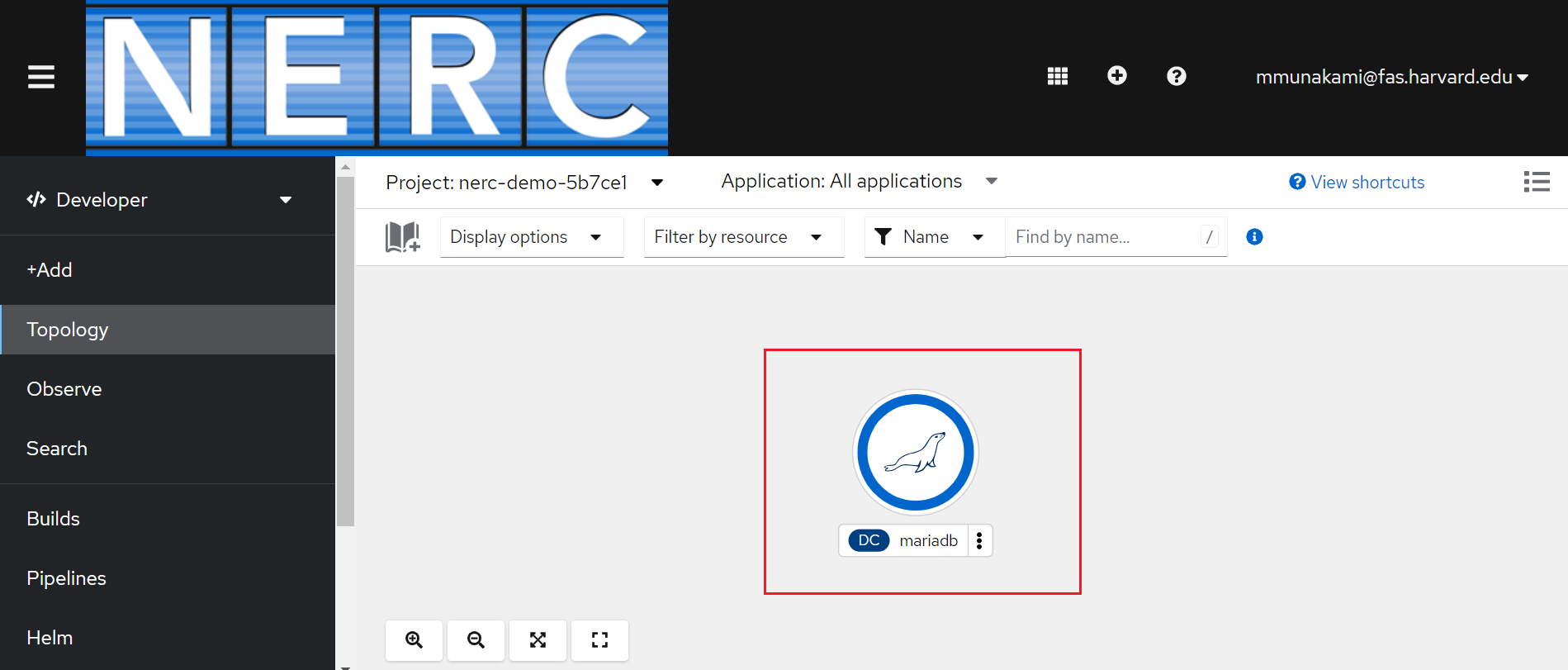
View the MariaDB service in the Topology view as shown below:
For Additional resources
For more options and customization please read this.