OpenStack CLI
References
OpenStack Command Line Client(CLI) Cheat Sheet
The OpenStack CLI is designed for interactive use. OpenStackClient (aka OSC) is a command-line client for OpenStack that brings the command set for Compute, Identity, Image, Object Storage and Block Storage APIs together in a single shell with a uniform command structure. OpenStackClient is primarily configured using command line options and environment variables. Most of those settings can also be placed into a configuration file to simplify managing multiple cloud configurations. Most global options have a corresponding environment variable that may also be used to set the value. If both are present, the command-line option takes priority.
It's also possible to call it from a bash script or similar, but typically it is too slow for heavy scripting use.
Command Line setup
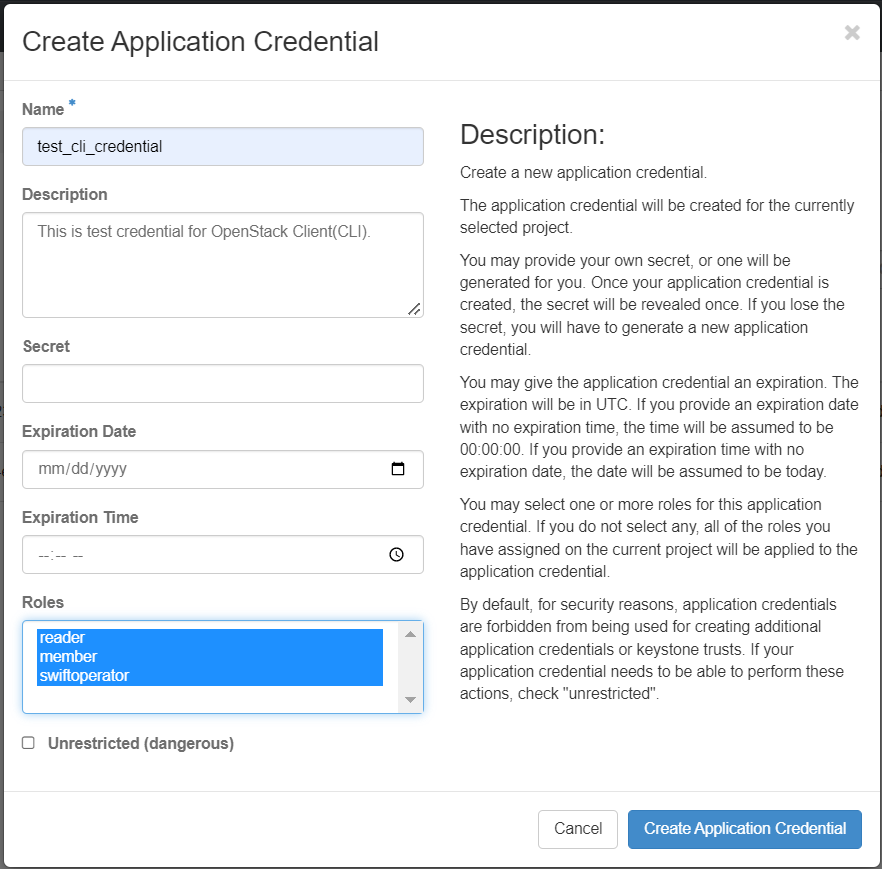
To use the CLI, you must create an application credentials and set the appropriate environment variables.
You can download the environment file with the credentials from the OpenStack dashboard.
-
Log in to the NERC's OpenStack dashboard, choose the project for which you want to download the OpenStack RC file.
-
Navigate to Identity -> Application Credentials.
-
Click on "Create Application Credential" button and provide a Name and Roles for the application credential. All other fields are optional and leaving the "Secret" field empty will set it to autogenerate (recommended).
Important Note
Please note that an application credential is only valid for a single project to access multiple projects you need to create an application credential for each. You can switch projects by clicking on the project name at the top right corner and choosing from the dropdown under "Project".
After clicking "Create Application Credential" button, the ID and
Secret will be displayed and you will be prompted to Download openrc file
or to Download clouds.yaml. Both of these are different methods of
configuring the client for CLI access. Please save the file.
Configuration
The CLI is configured via environment variables and command-line options as listed in Authentication.
Configuration Files
OpenStack RC File
Find the file (by default it will be named the same as the application
credential name with the suffix -openrc.sh where project is the name of your
OpenStack project).
Source your downloaded OpenStack RC File:
source app-cred-<Credential_Name>-openrc.sh
Important Note
When you source the file, environment variables are set for your current shell. The variables enable the openstack client commands to communicate with the OpenStack services that run in the cloud. This just stores your entry into the environment variable - there's no validation at this stage. You can inspect the downloaded file to retrieve the ID and Secret if necessary and see what other environment variables are set.
clouds.yaml
clouds.yaml is a configuration file that contains everything needed to
connect to one or more clouds. It may contain private information and is
generally considered private to a user.
For more information on configuring the OpenStackClient with clouds.yaml
please see the OpenStack documentation.
Install the OpenStack command-line clients
For more information on configuring the OpenStackClient please see the OpenStack documentation.
Tip
Install the OpenStack CLI by following the instructions specific to your operating system:
For Ubuntu (Debian-based):
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3-openstackclient
For CentOS (Red Hat-based):
sudo yum install python3-openstackclient
Alternatively, you can install it via pip:
pip install python-openstackclient
OpenStack Hello World
Generally, the OpenStack terminal client offers the following methods:
-
list: Lists information about objects currently in the cloud.
-
show: Displays information about a single object currently in the cloud.
-
create: Creates a new object in the cloud.
-
set: Edits an existing object in the cloud.
To test that you have everything configured, try out some commands. The following command lists all the images available to your project:
openstack image list
+--------------------------------------+---------------------+--------+
| ID | Name | Status |
+--------------------------------------+---------------------+--------+
| a9b48e65-0cf9-413a-8215-81439cd63966 | MS-Windows-2022 | active |
| cfecb5d4-599c-4ffd-9baf-9cbe35424f97 | almalinux-8-x86_64 | active |
| 263f045e-86c6-4344-b2de-aa475dbfa910 | almalinux-9-x86_64 | active |
| 41fa5991-89d5-45ae-8268-b22224c772b2 | debian-10-x86_64 | active |
| 99194159-fcd1-4281-b3e1-15956c275692 | fedora-36-x86_64 | active |
| 74a33f77-fc42-4dd1-a5a2-55fb18fc50cc | rocky-8-x86_64 | active |
| d7d41e5f-58f4-4ba6-9280-7fef9ac49060 | rocky-9-x86_64 | active |
| 75a40234-702b-4ab7-9d83-f436b05827c9 | ubuntu-18.04-x86_64 | active |
| 8c87cf6f-32f9-4a4b-91a5-0d734b7c9770 | ubuntu-20.04-x86_64 | active |
| da314c41-19bf-486a-b8da-39ca51fd17de | ubuntu-22.04-x86_64 | active |
+--------------------------------------+---------------------+--------+
If you have launched some instances already, the following command shows a list of your project's instances:
openstack server list --fit-width
+--------------------------------------+------------------+--------+----------------------------------------------+--------------------------+--------------+
| ID | Name | Status | Networks | Image | Flavor |
+--------------------------------------+------------------+--------+----------------------------------------------+--------------------------+--------------+
| 1c96ba49-a20f-4c88-bbcf-93e2364365f5 | vm-test | ACTIVE | default_network=192.168.0.146, 199.94.60.4 | N/A (booted from volume) | cpu-su.4 |
| dd0d8053-ab88-4d4f-b5bc-97e7e2fe035a | gpu-test | ACTIVE | default_network=192.168.0.146, 199.94.60.4 | N/A (booted from volume) | gpu-su-a100.1 |
+--------------------------------------+------------------+--------+----------------------------------------------+--------------------------+--------------+
How to fit the CLI output to your terminal?
You can use --fit-width at the end of the command to fit the output to your
terminal.
If you don't have any instances, you will get the error list index out of
range, which is why we didn't suggest this command for your first test:
openstack server list
list index out of range
If you see this error:
openstack server list
The request you have made requires authentication. (HTTP 401) (Request-ID: req-6a827bf3-d5e8-47f2-984c-b6edeeb2f7fb)
Then your environment variables are likely not configured correctly.
The most common reason is that you made a typo when entering your password. Try sourcing the OpenStack RC file again and retyping it.
You can type openstack -h to see a list of available commands.
Note
This includes some admin-only commands.
If you try one of these by mistake, you might see this output:
openstack user list
You are not authorized to perform the requested action: identity:list_users.
(HTTP 403) (Request-ID: req-cafe1e5c-8a71-44ab-bd21-0e0f25414062)
Depending on your needs for API interaction, this might be sufficient.
If you just occasionally want to run 1 or 2 of these commands from your terminal, you can do it manually or write a quick bash script that makes use of this CLI.
However, this isn't a very optimized way to do complex interactions with OpenStack. For that, you want to write scripts that interact with the python SDK bindings directly.
Pro Tip
If you find yourself fiddling extensively with awk and grep to extract things like project IDs from the CLI output, it's time to move on to using the client libraries or the RESTful API directly in your scripts.