Kubernetes Overview
Kubernetes, commonly known as K8s is an open sourced container orchestration tool for managing containerized cloud-native workloads and services in computing, networking, and storage infrastructure. K8s can help to deploy and manage containerized applications like platforms as a service(PaaS), batch processing workers, and microservices in the cloud at scale. It reduces cloud computing costs while simplifying the operation of resilient and scalable applications. While it is possible to install and manage Kubernetes on infrastructure that you manage, it is a time-consuming and complicated process. To make provisioning and deploying clusters much easier, we have listed a number of popular platforms and tools to setup your K8s on your NERC's OpenStack Project space.
Kubernetes Components & Architecture
A Kubernetes cluster consists of a set of worker machines, called nodes, that run containerized applications. Every cluster has at least one worker node. The worker node(s) host the Pods that are the components of the application workload.
The control plane or master manages the worker nodes and the Pods in the cluster. In production environments, the control plane usually runs across multiple computers and a cluster usually runs multiple nodes, providing fault-tolerance, redundancy, and high availability.
Here's the diagram of a Kubernetes cluster with all the components tied together.
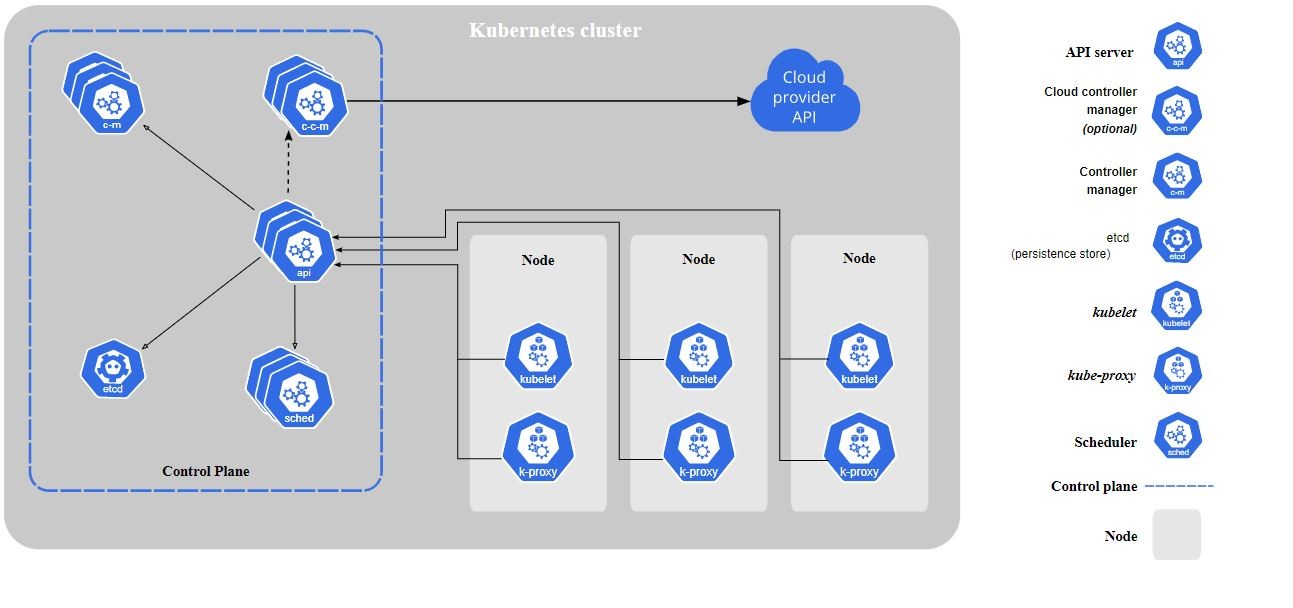
Kubernetes Basics workflow
Development environment
-
Minikube is a local Kubernetes cluster that focuses on making Kubernetes development and learning simple. Kubernetes may be started with just a single command if you have a Docker (or similarly comparable) container or a Virtual Machine environment. For more read this.
-
Kind is a tool for running local Kubernetes clusters utilizing Docker container "nodes". It was built for Kubernetes testing, but it may also be used for local development and continuous integration. For more read this.
-
MicroK8s is the smallest, fastest, and most conformant Kubernetes that tracks upstream releases and simplifies clustering. MicroK8s is ideal for prototyping, testing, and offline development. For more read this.
-
K3s is a single <40MB binary, certified Kubernetes distribution developed by Rancher Labs and now a CNCF sandbox project that fully implements the Kubernetes API and is less than 40MB in size. To do so, they got rid of a lot of additional drivers that didn't need to be in the core and could easily be replaced with add-ons. For more read this.
To setup a Multi-master HA K3s cluster using k3sup(pronounced ketchup) read this.
To setup a Single-Node K3s Cluster using k3d read this and if you would like to setup Multi-master K3s cluster setup using k3d read this.
-
k0s is an all-inclusive Kubernetes distribution, configured with all of the features needed to build a Kubernetes cluster simply by copying and running an executable file on each target host. For more read this.
Production environment
If your Kubernetes cluster has to run critical workloads, it must be configured to be resilient and higly available(HA) production-ready Kubernetes cluster. To setup production-quality cluster, you can use the following deployment tools.
-
Kubeadm performs the actions necessary to get a minimum viable, secure cluster up and running in a user friendly way. Bootstrapping cluster with kubeadm read this and if you would like to setup Multi-master cluster setup using Kubeadm read this.
-
Kubespray helps to install a Kubernetes cluster on NERC OpenStack. Kubespray is a composition of Ansible playbooks, inventory, provisioning tools, and domain knowledge for generic OS/Kubernetes clusters configuration management tasks. Installing Kubernetes with Kubespray read this.
To choose a tool which best fits your use case, read this comparison.





